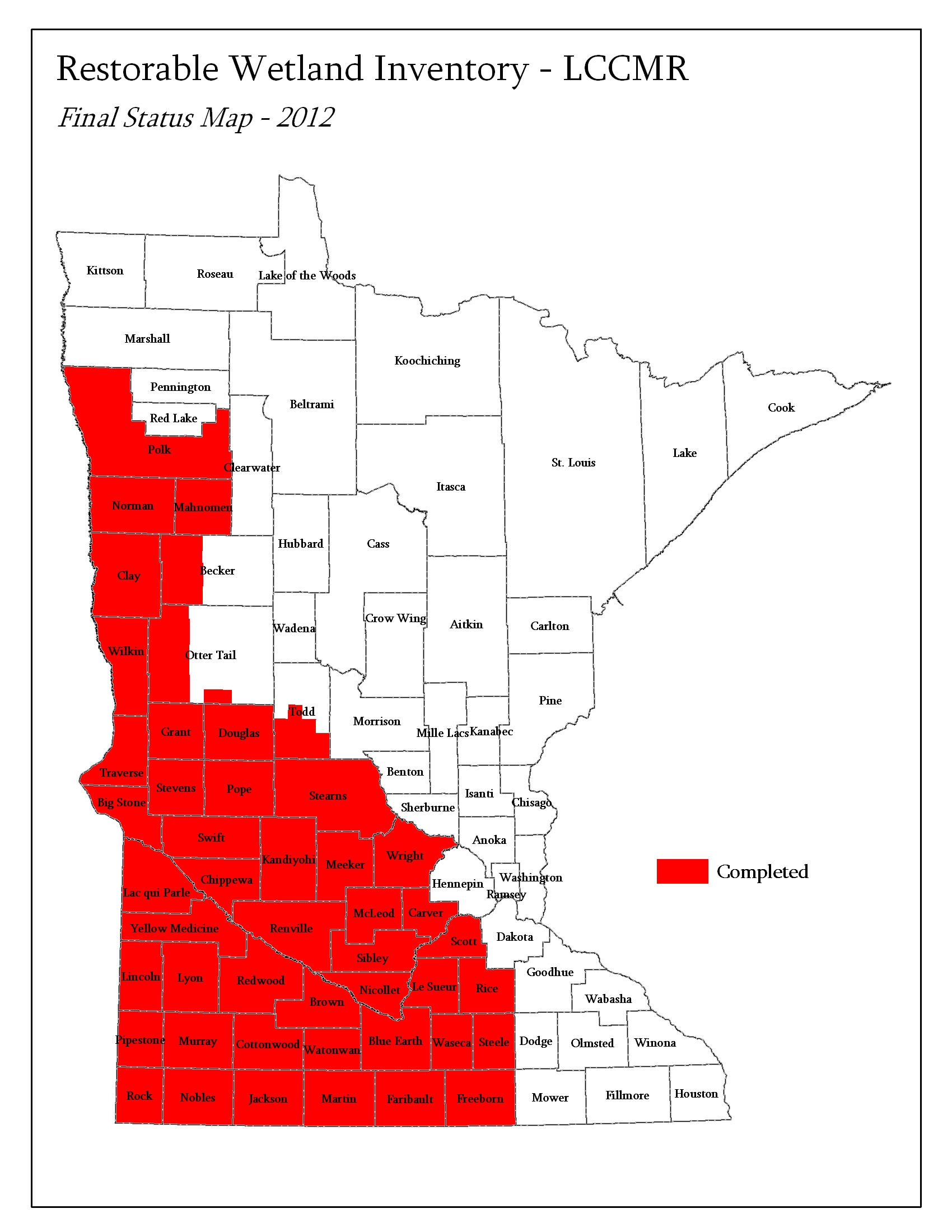
In October 2000, a Restorable Wetlands Working Group formed to begin mapping all of the restorable wetlands in the glaciated tallgrass Prairie Pothole Region of Minnesota and Iowa. Today, fewer than 10% of the original wetlands - once of unparalleled importance to continental waterbird populations - are left in existence. Fortunately, wetlands once drained for agriculture may be restored to many of their historic functions. Restoration of multiple wetland functions is of utmost effectiveness when focused at priority restoration landscapes, therefore data on the historic distribution of wetlands is an integral part of developing strategic regional habitat restoration plans.
Opportunistic wetland restorations often fail to attain out expectations for wetland function. Nevertheless, between $70 - $100,000,000 are spent annually in Minnesota for wetland restoration. A strategic plan for wetland restoration can make these expenditures more effective; however, a strategic wetland restoration plan requires a priori information on the distribution and extent of restorable wetlands. The collective goal of the Restorable Wetlands Working Group is the eventual development of a set of multi-agency decision support tools that collectively comprise a comprehensive environmental management plan for wetlands - all based on the same base data layers and developed in joint consultation. An effort is underway to delineate restorable wetlands in all intensively farmed areas of MN and IA.

A pilot project determined the best technique to map drained wetlands in agricultural landscapes was photointerpretation. This pilot project evaluated the accuracy of three potential delineation techniques: digital hydric soils databases, digital elevation models, and manual stereoscopic photointerpretation on high-altitude color infrared aerial photographs. The project covered nearly 4,000 square miles of different land forms and wetland characteristics. After mapping was completed, some 1,500 drained wetlands were observed in the field to assess the accuracy of each technique. Only photointerpretation provided reliable results.
One area that fell into the pilot study was the Okabena quadrangle in east-central Jackson County in Minnesota. Okabena vividly illustrates the potential of humans to alter the natural landscape. While Okabena historically encompassed more than 8,940 acres of depressional wetland - 27% of the total area of Okabena - after nearly 100 years of agricultural drainage only 1,280 acres of those original wetlands remain, representing an 86% reduction. When empirical models used to estimate duck pairs on individual wetlands are applied to the change from historic to current wetland habitat within Okabena, they estimate a 92% reduction in the habitat potential for common dabbling duck species.
The Okabena quadrangle's wetland density once exceeded that of most of the remaining U.S. Prairie Pothole Region. Without strong incentives for wetland conservation and effective methods to delineate high-priority landscapes for restoration, the Okabena quadrangle foretells one possible future for much of the mixed-grass Prairie Pothole Region further west.
Contact Information:
Ducks Unlimited, Inc.
Great Plains Regional Office
GIS Deptartment
(701)355-3500
Ducks Unlimited uses cookies to enhance your browsing experience, optimize site functionality, analyze traffic, and deliver personalized advertising through third parties. By continuing to use this site, you agree to our use of cookies. View Privacy Policy